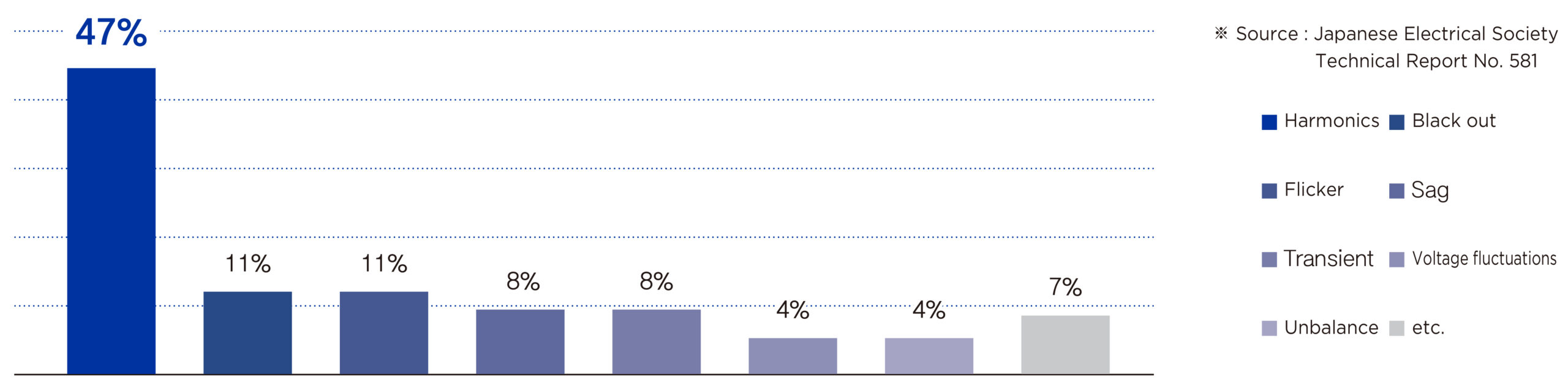
Harmonic generation is increasing as rectifiers, inverters, LEDs, landscape lighting, PCs, motors, and automation facilities with high harmonics in the power system increase. These harmonics cause damage in various forms, including increased loss of electrical equipment, reduced efficiency, malfunction, shorter life expectancy, and heat generation.
| Device | DC subway substation, electrochemical, etc. | Alternating-current electric railway vehicle | General-purpose inverters, elevators, refrigeration and air conditioners, etc. |
| UPS, Power supply for communication, distributed device for grid connection | Reactive power compensator (SVC), lighting device, heater | Electric motors (for rolling, cement, AC railway vehicles) | |
| For steelmaking | etc. (LED, induction, Electric vehicle charging device) | ||
| Types of circuits | 3 phase bridge | Single phase bridge | 3 phase/Single phase bridge |
| 3 phase/Single phase bridge (PWM control) | rnating current power controller | Cyclone converter | |
| Alternating current arc furnace | |||
Harmonics cause various forms of damage to the power system and various electrical installations, such as increased losses, increased temperature, and breakdown of insulation.
| Immediately · Short term | Resonance caused by voltage and current | Power factor reduction | Decrease in power generation |
| Neutral over current | Overcurrent of cables, transformers, generators, power capacitors | Unpredictable shutdown of the protection system | |
| Malfunction of precision control device | Increased facility noise and vibration | Current and voltage distortion | |
| Induced disturbance of telephone and communication lines | Overdesign (wires, transformers, power capacitors) | ||
| Mid · Long-term | Reduce motor and transformer life | Acceleration of deterioration of dielectric materials and insulation materials | Rising economic costs |
| Transformer | Power quality technology | Overheating, increased noise | Capacity reduction |
| Insulation breakdown | |||
| Wires and conductors | Overheating | Corona outbreak | Neutral over current |
| Capacity reduction | Insulation breakdown | Skin Effect | |
| Rotating machine | Overheating | Decrease in efficiency | Shortened device lifespan |
| Tog uneven | Vibrational torque | ||
| Capacitor for power | Overheating | Over-resonance | Overcurrent |
| Overvoltage insulation explosion | |||
| Overcurrent | Abrupt stop | Inaccurate measurement | Non-integer harmonic generation |
| Malfunction | Frequent part failure | ||
| Circuit breaker · Other | Ampacity reduction | Noise, Vibration | Acceleration of life deterioration |
| Drop in power factor | Decreased fuse capacity | Signal, communication failure | |
Iron loss increase rate
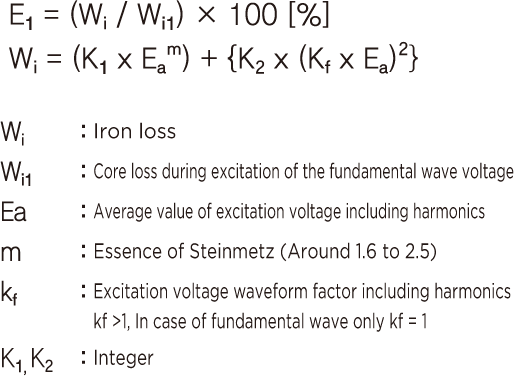
Copper loss increase rate

Three-phase load
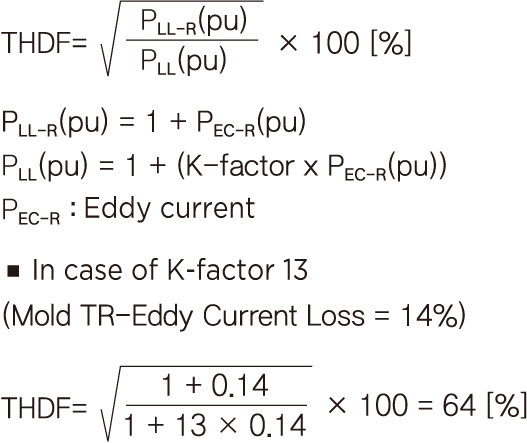
Transformer winding temperature rise

To prevent electrical damage from harmonics, harmonics standards are being enforced globally.

| Field | Before mendment | After mendment |
|---|---|---|
| Incoming transfer facility | Transformers are selected in consideration of the place of use, economic feasibility, and electrical characteristics, but when installed inside a building, a transformer with more than standard consumption efficiency should be used. | When selecting a transformer, the place of use, load characteristics, efficiency, safety, etc. must be considered, and a standard efficiency transformer is used. However, in the case of facilities with a high harmonic generation load ratio, a transformer with harmonic attenuation function or a transformer with equivalent or better performance can be used to improve power quality and reduce power loss. |

| Harmonics (n) | Equipment Classification | |||
| Balanced 3-phase equipment, Tools, sound equipment, Household appliances (A) | Portable device, Arc welding machine (A) | Lighting equipment (A) | PC, Monitor, TV, Refrigerator, Freezer (Under 600W) (A) | |
| Odd Harmonics | ||||
| 3 | 2.30 | 3.45 | 30 X Power factor | 2.30 |
| 5 | 1.14 | 1.71 | 10 | 1.14 |
| 7 | 0.77 | 1.155 | 7 | 0.77 |
| 9 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 5 | 0.40 |
| 11 | 0.33 | 0.495 | 3 | 0.33 |
| 13 | 0.21 | 0.315 | 3 | 0.21 |
| 15 ≤ n ≤ 39 | 0.15 × 15/n | 0.225 × 15/n | 3 | 0.15 × 15/n |
| Even Harmonics | ||||
| 2 | 1.08 | 1.62 | 2 | - |
| 4 | 0.43 | 0.645 | - | - |
| 6 | 0.30 | 0.45 | - | - |
| 8 ≤ n ≤ 40 | 0.23 × 8/n | 0.345 × 8/n | - | - |
| Bus voltage V at PCC | Individual harmonic (%) | Total harmonic distortion THD (%) |
|---|---|---|
| V ≤ 1.0 kV | 5.0 | 8.0 |
| 1 kV < V ≤ 69 kV | 3.0 | 5.0 |
| 69 kV < V ≤ 161 kV | 1.5 | 2.5 |
| 161 kV < V | 1.0 | 1.5a |
| Maximum harmonic current distortion in percent of 𝐼𝐿 | ||||||
| Individual harmonic order (odd harmonics)a,b | ||||||
| 𝐼𝑆𝐶 / 𝐼𝐿 | 3 ≤ ℎ<11 | 11 ≤ ℎ<17 | 17 ≤ ℎ<23 | 23 ≤ ℎ<35 | 35 ≤ ℎ ≤ 50 | TDD |
| <20c | 4.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 5.0 |
| 20<50 | 7.0 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 8.0 |
| 50<100 | 10.0 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 12.0 |
| 100<1000 | 12.0 | 5.5 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 15.0 |
| >1000 | 15.0 | 7.0 | 6.0 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 20.0 |